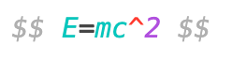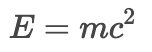Markdown may seem like a simple, old-school way of formatting text, but it’s actually one of the most powerful tools you can use for note-taking, especially in a dynamic environment like medical school. If you’ve already started using Obsidian, you know that it’s a highly flexible, markdown-based note-taking app that allows you to create interconnected notes, making it easier to navigate the massive amount of information you encounter in medical studies. But to truly make the most of Obsidian, learning markdown is essential.
Markdown might appear intimidating at first, especially if you’re not familiar with code or plain-text formatting. However, it’s a breeze once you get the hang of it.
Starting medical school? Check out our must have phone apps to impress, succeed, and learn effectively during your pre-clerkship and clinical rotations.
This guide will walk you through everything you need to know to use markdown effectively in Obsidian, so you can structure your notes, organize your learning, and maximize retention, all while staying efficient and focused.
Why Markdown Matters in Obsidian
Markdown is a lightweight markup language that uses easy-to-learn syntax to format text. Unlike traditional text editors like Word or Google Docs where formatting is hidden behind menus and toolbars, markdown allows you to control the look and structure of your notes with a few simple symbols.
This simplicity is one of markdown’s greatest strengths, and can help makes your notes cleaner, easier to organize, and more adaptable for future use.
Every single feature, from headings to links, revolves around markdown. Once you get the hang of it, you’ll find that using markdown is much faster and more intuitive than dealing with traditional word processors, making it ideal for medical school’s fast-paced, high-volume note-taking.
Not finding your study strategy works? Check out our picks for the best note-taking apps for medical students to help find what works for you, or explore our guide to mastering Notability.
Getting Started with Markdown
Before diving into more advanced uses of markdown, let’s cover the basics. These simple formatting tools will make up the bulk of your note-taking in Obsidian.
1. Headings: Structure Your Notes
Headings are an essential part of keeping your notes organized. Whether you’re creating notes, summarizing lectures, or reviewing pathology/diagrams, headings help break your notes into easily digestible sections.
To create a heading, type a # symbol followed by the text of the heading. The number of # symbols you use determines the heading size. For instance, using ## before the text will generate a level two heading, and ### will produce a level three heading.

This would render as:
Using consistent headings throughout your notes allows you to quickly scan through long documents and find the information you need. For medical school, this is particular useful when you’re reviewing large volumes of material, such as during exams or rounds.
2. Bold and Italics: Emphasize Key Points
Highlighting important information is easy in markdown. Use bold for key terms, diagnoses, or important takeaways, and italics for secondary information or less critical details. You may also use your standard keyboard shortcuts to bold or italicize.
In practice, you might bold important terms, and italicize peculiar pathogenic mechanisms or treatments. This helps you quickly identify the most critical information when you’re reviewing your notes before an exam or patient encounter.
Other text formatting options including striking through (~~striked out text~~), highlighting text (==highlighted text==), or a combination of any of the text formatting options.
3. Lists: Organizing Information Logically
Lists are essential for organizing symptoms, treatment plans, or step-by-step processes. Whether you’re outlining the physical exam steps or listing the side effects of a drug, markdown allows for easy and intuitive list-making.
Unordered lists use ‘-' or ‘*’ :
Ordered lists use numbers:
You can also create nested lists by indenting:
These lists are particularly useful when you’re learning about complex systems with multiple components, such as pharmacology, where you need to compare drugs, mechanisms, dosing, and side effects.
4. Links: Connecting Ideas Across Notes
One of the most powerful aspects of Obsidian is its ability to create internal links between notes. Medicine is inherently interconnected, wherein knowledge of one system often relates to others. Understanding these relationships is key to becoming a competent clinician. Markdown makes linking concepts across different notes seamless.
To link to another note in Obsidian, use double brackets:
This simple command allows you to connect different topics. For instance, when studying renal physiology, you can link directly to your notes on hypertension or electrolyte imbalances. Adding an exclamation point (!) in front of a linked page will display the full page within your current note.
- Linking concepts: The utility lies in linking connected topics. For example, if you’re reviewing diabetes and discussing complications, you can link to notes on nephropathy and retinopathy.
- Connecting clinical cases: If you’re writing up patient cases, you can link to theoretical notes about the conditions they have, making it easy to navigate between real-life cases and the underlying science.
Eventually, your graph will become an web of ideas that can help you understand how concepts are connected together.

5. Images: Adding Visuals to Your Obsidian Notes
As a medical student, you’ll often rely on visuals to reinforce your learning. Anatomy diagrams, diagnostic flowcharts, and pathology images can be crucial in understanding complex subjects. Markdown makes it easy to embed images directly in your notes.
To add an image, copy a photo and directly paste it into your note.
If you want to re-insert a note that already exists in your Obsidian vote, you can use the following syntax to re-insert an image:
If the image is in your vault, the photo will be automatically inserted in-line as demonstrated:
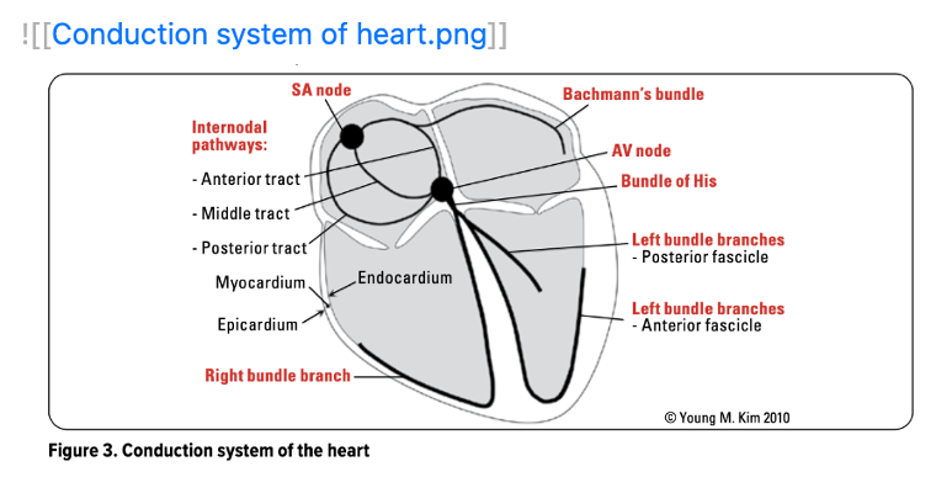
This feature allows you to integrate images into your study notes seamlessly. Whether you’re working through an anatomy lecture or revisiting a clinical case, having visuals directly in your notes will help reinforce improving and improve retention.
Advanced Markdown Features
Once you’re comfortable with the basics, you can start incorporating some of markdown’s more advanced features to take your note-taking to the next level. These tools will help you create more detailed, comprehensive notes that are easier to study from.
1. Blockquotes: Highlight Key Information
Blockquotes are perfect for pulling out important quotes, definitions, or guidelines from your readings or lectures. In markdown, a blockquote is created using the > symbol in front of the text that you want highlighted.

Use blockquotes to set off particularly important information, such as textbook definitions, key research findings, or clinical guidelines. This makes it easy to scan through your notes and identify high-yield information quickly.
2. Code Blocks and Formulas: Using Markdown for Equations
Medical students who are studying fields like pharmacology, biochemistry, or statistics might encounter complex formulas and equations. Luckily, markdown allows you to create code blocks and write out LaTeX equations.
For equations, Obsidian supports LaTeX, which is especially useful for writing out pharmacokinetics formulas, for example:
Would render out to this:
3. Tables: Organizing Comparative Data
Tables are a great way to compare treatments, symptoms, or lab values. While markdown tables are basic, they are incredibly useful for organizing complex data in a clear, structured way.
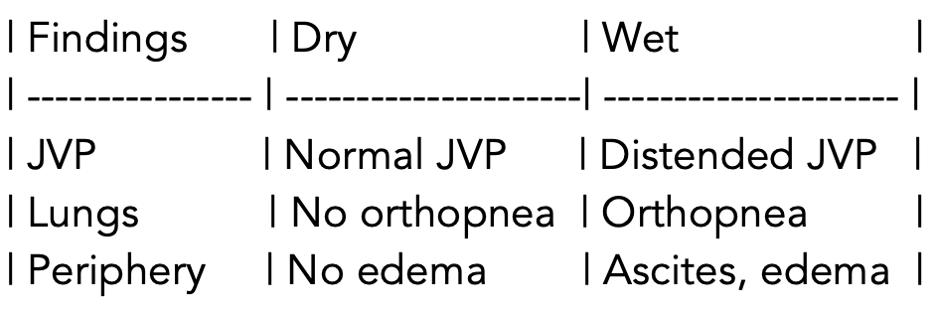
The syntax for tables looks like this:
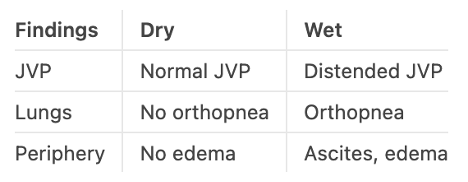
Which would render like this:
Cells don’t need to be perfectly aligned with the columns. Each header row must have at least two hyphens.
You can use tables to organize comparative data across topics. For example, when studying different types of medications, you could compare their indications, mechanisms of action, dosing, and side effects.
4. Tasks Lists: Tracking Your Progress
Obsidian also allows you to create simple task lists, which can be useful for staying organized with your studies. Whether it’s tracking what topics you’ve reviewed or creating a checklist for assignments, task lists help keep you on top of your responsibilities.
To create a task list, use the following syntax:
Which will render like this:
Task lists allow you to visually track what you’ve accomplished and what’s still pending. If you’re a medical student juggling multiple subjects, assignments, and clinical responsibilities, this can be a lifesaver.
5. Callouts: Seamless Flow
One of my favourite features is callouts, which allows you to include additional content without breaking the flow within your notes.
To create a callout, use the following syntax:
Which would render like this:
Within a callout block, you can also add internal links and embed files. You can additional change the title of your callout block, create foldable callouts, nested callouts, or create different callout types e.g. “note”, “abstract”, “info”, “tip”, “question”, “failure”, “example”, etc. Check out Obsidian’s official guide on Callouts which elaborates on these details further.
Customizing Your Markdown Workflow in Obsidian
Now that you’ve learned the essentials of markdown, it’s time to start thinking about how to customize it for your workflow in medical school. The flexibility of Obsidian means you can tailor your note-taking to fit your study habits, clinical work, and exam preparation.
1. Developing an Obsidian Note Template
To keep your notes consistent and efficient, consider developing a template that you can use across all your subjects. Here’s a basic example of a medical school note template:

Using a template like this will save you time and ensure that all of your notes are thorough and well-organized, making studying more efficient.
2. Leveraging Tags and Links
Tags and links are incredibly powerful tools in Obsidian. By tagging your notes with relevant keywords, you can easily group related topics across subjects. For example, if you tag all notes related to cardiology with #cardiology, you’ll be able to view all of your cardiology notes in one place.
Similarly, linking between notes helps you build a web of knowledge, making it easier to connect the dots across different systems and topics. This interconnectedness is especially important in medical school, where understanding the relationships between different systems is often key to understanding the nuance of diagnosing and treating patients with multiple diseases.
If you’re looking for additional basic or advanced Obsidian techniques, check out this guide here.
Final Thoughts
Markdown is a powerful tool that can transform the way you take notes in medical school. Its simplicity, combined with Obsidian’s rich features, makes it the ideal system for organizing and navigating the vast amounts of information you’ll encounter throughout your studies.
By mastering markdown, you’ll be able to create notes that are clear, organized, and highly personalized to your study style. With the added benefits of linking, tagging, and embedding images or tables, you can make your notes an interactive, interconnected resource that helps you retain and apply the knowledge you need to succeed in both exams and clinical practice.
Heading into the OR? These top surgical rotation apps will help you prep smarter, learn faster, and feel more in control in the OR.